I. Number Systems and Arithmetic

Horse Race: Probability and Addition
A game where participants begin by choosing a toy horse (numbered 2-12). They take turns rolling two dice, adding the pips, and advancing the corresponding horse. This game gives practice in addition and offers insight into probabilities.
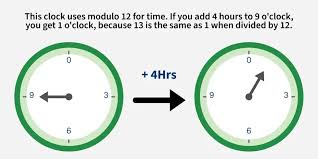
Number Bases and Modular Arithmetic
We deconstruct numbers into their ones, tens, hundreds, and thousands places and introduce different number bases. We count using models and learn to count to 31 on one hand using base 2. This project builds understanding of number systems.
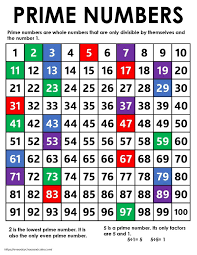
Experiments with Prime Numbers
Using a 1-100 grid, we cross out multiples of 2, 3, 5, 7, etc., with different colors. We also experiment with wrapping the grid to a cylinder or torus. This helps develop an understanding of number factorization.
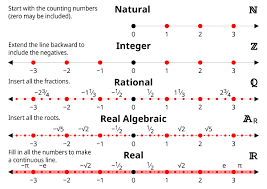
Introduction to the Real Number Line
Covers positive and negative numbers, rational numbers, and the countability of integers and rationals. We explore irrational numbers, the Pythagorean Theorem, the irrationality of √2, and transcendental numbers. This introduces students to numbers beyond integers.

Palindromes
Participants repeatedly add a number to its reverse until a palindrome is obtained. This project helps develop facility with addition without memorization.
II. Geometry and Topology
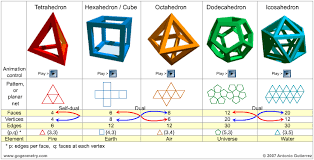
The Euler Characteristic
An experiment with the Zomes kit. We define "convex polyhedron" and use 5 pre-built Platonic solids to compute the Euler characteristic (vertices - edges + faces). This helps build geometric intuition.
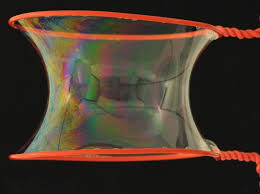
Soap Bubbles and Minimal Surfaces
Using a tub of soap solution and Zomes kit models, children guess what surface will result from dipping the models. They then test their hypotheses. This project helps build geometric intuition.
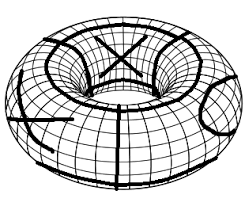
Games on Non-Flat Surfaces
Explore Tic-tac-toe and other puzzles and games on surfaces like the torus and Klein bottle. Tangrams are also used. This project helps develop geometric intuition.
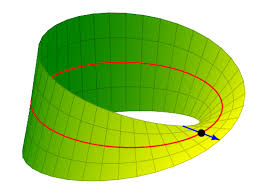
Experiments with the Mobius Strip
Learn how it's constructed and its difference from a cylinder. We experiment by cutting it along the center and the upper-third. This helps develop geometric intuition.
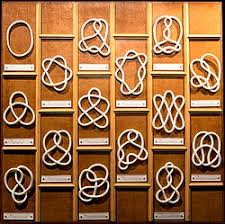
Introduction to Knot Theory
We define "knot" and the goal of Knot Theory. Activities include constructing various knots and links, working on puzzles, and viewing the "Not Knot" video. This project helps build visualization skills.
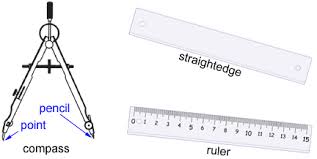
Geometric Constructions
Participants practice constructions with a straightedge and compass. We also construct an ellipse using string, pins, and a pencil. This project builds facility with geometric tools.

Introduction to Dimension
We use Zome models of a point, line, square, cube, and hypercube. We experiment with objects in Flatland and progress to three- and four-dimensional spaces. This helps develop geometric intuition.

Turning the Sphere Inside Out
We explore the concepts of sphere eversion by viewing "Outside In," a video that demonstrates how a sphere can be turned inside out by passing the surface through itself. This project helps develop geometric visualization.
III. Logic and Problem Solving

Logic Puzzles and Games
We develop strategies for solving problems and playing games. Puzzles include boat crossing, word problems, Rush Hour, Sudoku, Dots-and-Boxes, and Nim. This project helps develop logical thinking.
IV. Algebra, Functions, and Advanced Concepts
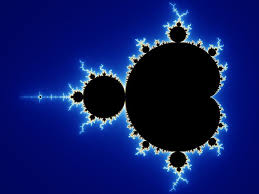
Fractals and Self-Similarity
We explore self-similarity in nature (ferns, broccoli) and construct the Koch snowflake and Sierpinski triangle. Using a computer, we explore the Mandelbrot set. This shows connections between math and natural phenomena.
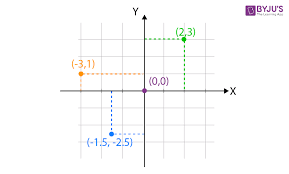
Cartesian Coordinates
This project focuses on describing the location of a point in the plane. It covers linear functions, graphing functions, and distances in Euclidean space. This introduces students to functions and non-Euclidean geometry.
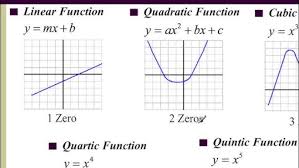
Algebra and Polynomial Equations
We introduce polynomial functions with real coefficients and draw graphs. We look at polynomial equations with simple integer solutions and discuss factoring.
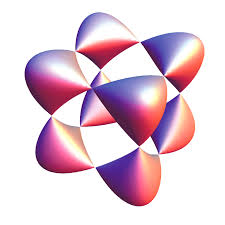
Algebraic Surfaces
Using the site Desmos, we explore algebraic surfaces. This project helps develop geometric visualization.
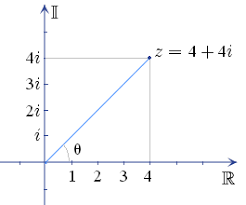
Complex Numbers
We use polynomial equations with no real solutions and fractals to introduce complex numbers. This provides the mathematical framework for the earlier project on fractals.
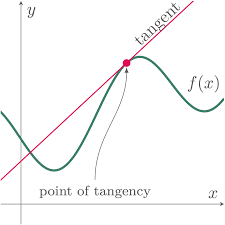
Introduction to Calculus
We cover measuring the slope of a line, tangent lines, inflection points, and the area under a curve. We also explore a paradox: an object with finite volume but infinite surface area.